- contact@mahiclinic.com


- Home
- Total Knee Replacement
- Knee Arthoscopy
- Hip Replacement
- More Info
Conditions
- Elbow
- Knee
Blog Details
- Home
- blog-details
A Comprehensive Guide on PCL Tear by Mahi Clinic
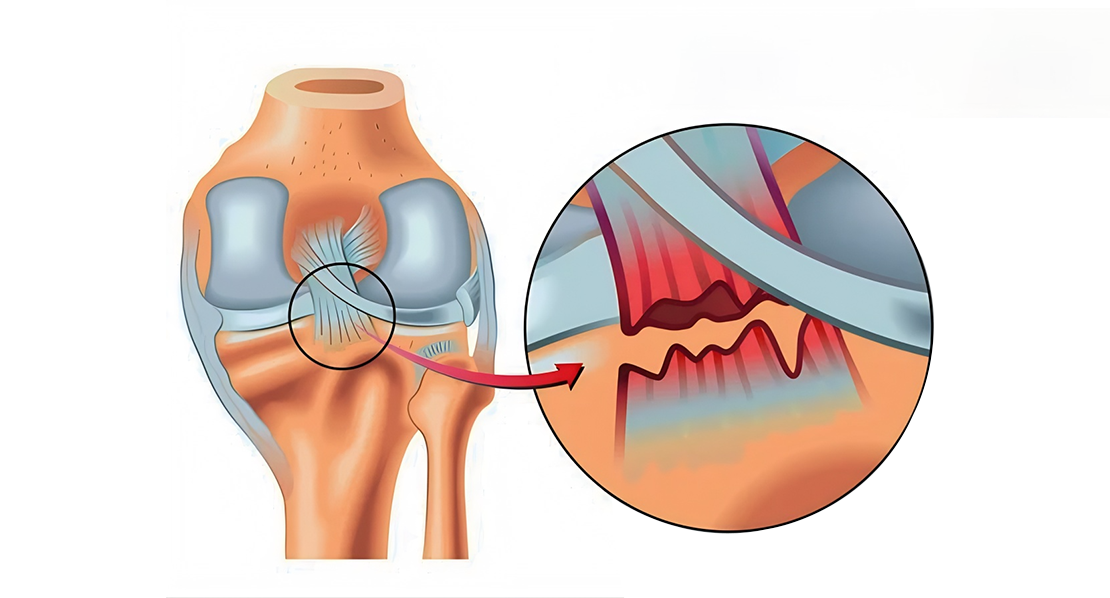
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a crucial component of the knee joint. It plays a vital role in stabilizing the knee and preventing it from moving too far backward. Although PCL tear are less common than anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries, they can significantly impact an individual's knee function and overall quality of life. This guide explores the anatomy, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for PCL tear, emphasizing prompt intervention and Clinician care Hospital (CCH) and Mahi Clinic's expertise under the guidance of Dr. Vijay kumar Sohanlal in managing this orthopaedic concern.
Anatomy and Function of the PCL
The PCL is one of the four major ligaments in the knee, situated at the back of the joint. It connects the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone) and is crucial for maintaining stability during various knee movements. The primary function of the PCL is to prevent the tibia from moving too far backward in relation to the femur. This ligament, along with others, contributes to the intricate balance that ensures smooth and controlled knee motion.
Epidemiology and Causes of PCL Tear
PCL tears are often the result of traumatic events, such as sports-related injuries, automobile accidents, or falls. The incidence of PCL tear is lower compared to ACL injuries, accounting for approximately 20% of all knee ligament injuries. People who participate in high-impact sports or activities that involve sudden stops or changes in direction are at increased risk of developing a PCL tear
Signs and Symptoms of a PCL Tear
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a PCL tear is crucial for early intervention. Common indicators include:
Pain: Pain in the knee joint.
Swelling: Swelling may occur.
Instability: A feeling of instability or the knee giving way, particularly when walking or descending stairs.
Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty in fully straightening or bending the knee.
Diagnostic Procedures for PCL Tear
Accurate diagnosis is important determining the severity of the PCL tear and guiding appropriate treatment. Diagnostic procedures may include:
Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the knee, evaluating range of motion, stability, and signs of injury.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI scans to visualize the extent of the PCL tear and assess any associated damage to surrounding structures.
Grades of PCL Tears and Their Implications
PCL tears are categorized into different grades based on their severity. Understanding these grades helps in tailoring an effective treatment plan. The grades include:
Grade I:
Partial Tear
Minimal damage to the ligament fibers.
Generally, the knee remains stable.Grade II:
Complete Isolated Tear.
Complete tear of the PCL.
Some loss of knee stability.Grade III:
Complete PCL tear with additional damage to surrounding structures.
Significant knee instability.Grade IV:
PCL Injury with Concomitant Damage to Another Knee Ligament.
Complete PCL tear with simultaneous damage to other ligaments.
Severe instability requiring comprehensive treatment.Treatment Options for PCL Tears
1. Non-Surgical Treatment for PCL Tears
The approach to PCL tears depends on the grade of the injury. Non-surgical methods may be effective for lower-grade tears (Grade I and some Grade II). These can include: Rest and Physical Therapy: Allowing the ligament to heal naturally with the guidance of a physical therapist.
1. Non-Surgical Treatment for PCL Tears
The approach to PCL tears depends on the grade of the injury. Non-surgical methods may be effective for lower-grade tears (Grade I and some Grade II). These can include: Rest and Physical Therapy: Allowing the ligament to heal naturally with the guidance of a physical therapist.
Bracing: Using a brace to stabilize the knee and prevent excessive movement. Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Managing pain and swelling with prescribed medications.
2. Surgical Reconstruction of PCL Tears
For more severe PCL tears (Grade II and above), surgical intervention may be recommended. Surgical options include:
The Robotic Surgical Method
Let's break down the key steps in a typical robotic knee replacement procedure to gain a better understanding of the robotic surgical process:
PCL Reconstruction: Rebuilding the torn ligament using grafts from the patient's own tissue or a donor.
Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to repair or reconstruct the PCL with small incisions.
Rehabilitation and Recovery after PCL Injury: Rehabilitation Goals and Strategies.
Regardless of the chosen treatment, rehabilitation is a crucial phase in the recovery process.Rehabilitation goals include:
Restoring Range of Motion: Gradual introduction of exercises to improve flexibility.
Strengthening Exercises: Focusing on building strength in the muscles surrounding the knee for enhanced stability.
Functional Training: Incorporating activities that mimic daily movements to ensure a smooth return to regular activities.
Recovery Timeline and Expectations
Recovery from a PCL tear varies based on the severity of the injury and the chosen treatment. Generally, rehabilitation may take several weeks, with a gradual return to normal activities. Full recovery may extend up to 3 to 6 months.
Preventing PCL Tears and Long-Term Management.
Injury Prevention Strategies for PCL TearsPreventing PCL tears involves adopting proactive measures, especially for individuals engaged in high-risk activities. Strategies include:
Strength and Conditioning: Building strength in the muscles around the knee through targeted exercises.
Proper Technique: Ensuring proper form and technique during sports and physical activities. Protective Gear: Wear appropriate protective gear, such as knee braces, to reduce the risk of injury.
Mahi Clinic and CCH with its commitment to comprehensive orthopedic care, offers a multidisciplinary approach to managing post-injury complications and ensuring long-term knee health. Our team, led by the renowned orthopedic expert Dr. Vijay kumar Sohanlal, specializes in personalized treatment plans, incorporating the latest advancements in orthopedic care.
At Mahi Clinic and CCH, we understand the physical and emotional impact of orthopedic injuries, including PCL tears. Dr. Vijay kumar Sohanlal, our esteemed orthopedic specialist, leads a team dedicated to providing expert guidance and individualized care. Our state-of-the-art facilities and commitment to excellence make Mahi Clinic and CCH a trusted partner in your journey towards recovery
In conclusion, navigating PCL tears involves a holistic approach, encompassing accurate diagnosis, tailored treatment plans, rehabilitation, and long-term preventive strategies. With CCH and Mahi Clinic's expert guidance, you can confidently address PCL tears and embark on a path to restored knee health.
- Knee
- Elbow
Leave a Reply